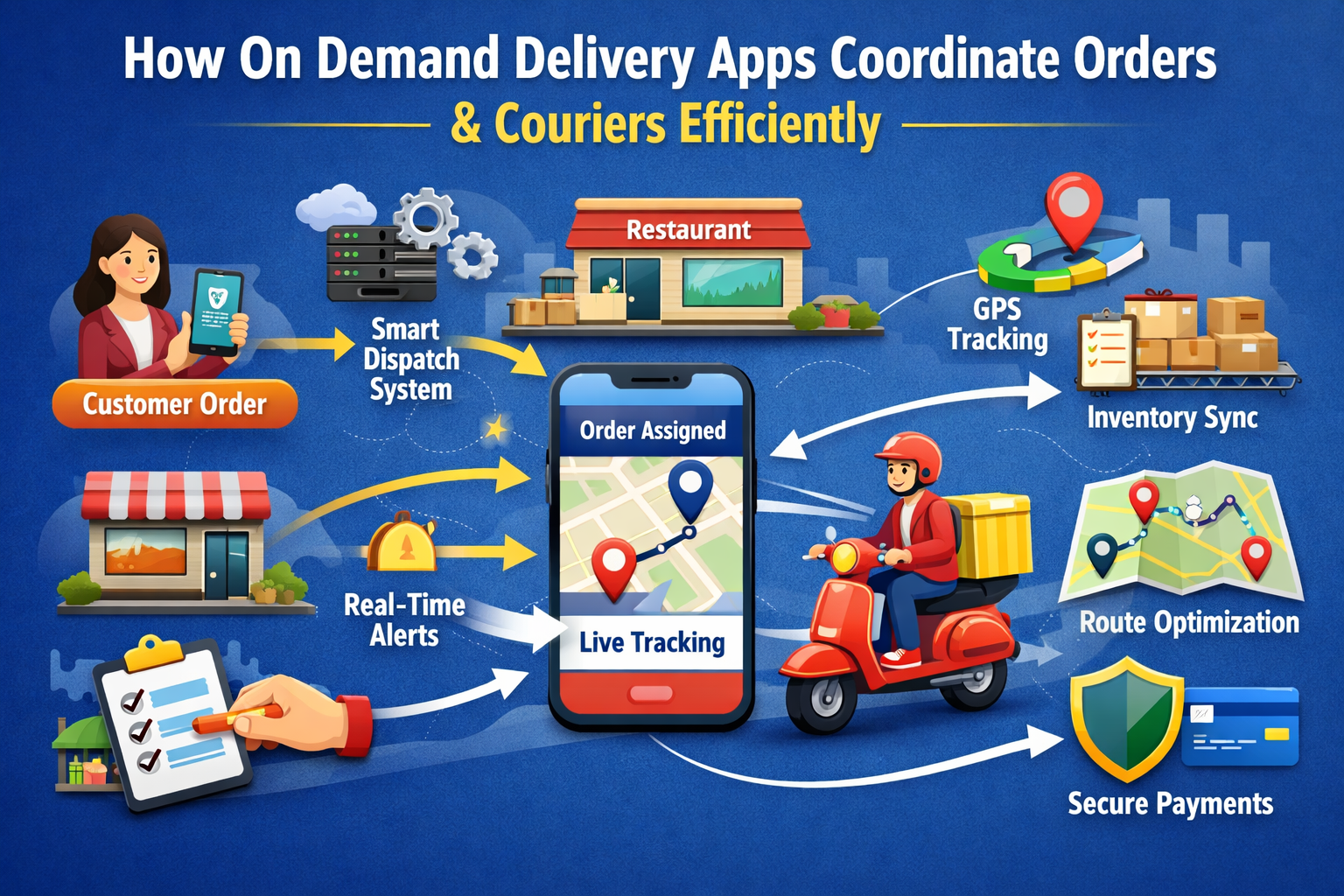
Modern consumers expect deliveries to arrive quickly, accurately, and with real-time visibility. Behind this convenience lies a sophisticated coordination system that connects customers, merchants, couriers, and logistics infrastructure. Delivery platforms rely on automation, intelligent dispatching, and scalable architecture to manage thousands of simultaneous transactions without delays. From order placement to final delivery confirmation, each step depends on synchronized digital workflows that reduce human intervention and optimize resource utilization across urban and regional distribution networks.
Understanding Real-Time Order Allocation In Platforms Delivery
Order allocation is one of the most critical processes in delivery ecosystems. When a customer places an order, the system must immediately identify the optimal courier based on proximity, availability, workload, and delivery priority. This requires event-driven backend services capable of processing data streams in milliseconds.
In on demand delivery app development, real-time allocation engines typically rely on queue-based processing systems that prevent conflicts between multiple couriers accepting the same task. These engines evaluate operational variables such as estimated preparation time, courier travel distance, and delivery deadlines.
A typical allocation workflow includes:
- Order validation and confirmation
- Vendor readiness estimation
- Courier availability scanning
- Distance calculation using mapping APIs
- Automated assignment confirmation
This orchestration ensures minimal idle time for couriers while maintaining delivery accuracy. Real-time allocation also reduces operational friction and supports scalability during peak demand periods.
How Intelligent Dispatch Algorithms Match Drivers Fast
Dispatch algorithms are responsible for pairing orders with the most suitable couriers. These algorithms rely heavily on optimization models, including nearest-neighbor logic, batching strategies, and dynamic priority scoring.
Machine learning models increasingly enhance dispatch accuracy by analyzing historical delivery patterns and predicting courier response times. The system continuously recalibrates assignments to minimize delays caused by traffic congestion or unexpected order surges.
Key factors considered in dispatch optimization include:
- Courier proximity to pickup location
- Current delivery queue of each courier
- Traffic density and road conditions
- Vendor preparation time estimates
- Delivery time commitments
By combining these variables, dispatch systems reduce delivery latency and improve utilization efficiency across the courier fleet.
Platforms built through on demand delivery app development often implement adaptive dispatching systems that evolve through real-time feedback loops. These loops allow platforms to maintain operational stability even when demand fluctuates significantly.
Role Of GPS Tracking In Courier Coordination Systems Efficiency
GPS tracking technology enables continuous visibility into courier movement, allowing delivery systems to update customers and vendors automatically. Real-time location updates are transmitted at frequent intervals, ensuring accurate delivery progress monitoring.
Courier coordination platforms use geolocation data to:
- Estimate arrival times dynamically
- Detect route deviations
- Trigger automated notifications
- Improve dispatch decisions
- Record delivery completion timestamps
Location intelligence also supports geofencing, which allows the system to detect when a courier enters or leaves predefined delivery zones. This capability improves accountability and enhances operational transparency.
In on demand delivery app development, GPS integration must be optimized for battery efficiency and network reliability. Developers often implement adaptive tracking intervals that adjust based on courier speed or delivery stage.
Reliable GPS coordination significantly reduces communication gaps between customers, vendors, and delivery personnel.
Managing Inventory Visibility Across Multiple Vendors In Apps
Delivery platforms that serve multiple merchants must maintain synchronized inventory data across distributed systems. Inventory visibility ensures customers only see items that are currently available, preventing order cancellations and customer dissatisfaction.
Real-time inventory synchronization typically relies on API-based communication between vendor systems and the delivery platform. Whenever stock levels change, updates are reflected instantly across customer-facing applications.
Common inventory management features include:
- Automated stock updates
- Low-inventory alerts
- Temporary item disabling
- Vendor dashboard controls
- Order-based stock deduction
Accurate inventory visibility improves fulfillment reliability and reduces operational disputes between vendors and customers.
Teams building such platforms often rely on mvp app development services to validate inventory synchronization workflows before scaling the system to support thousands of vendors.
Inventory coordination becomes increasingly complex as vendor networks expand across multiple cities or regions.
Optimizing Delivery Routes Using Predictive Analytics Tools Today
Route optimization directly affects delivery speed and operational cost efficiency. Instead of relying solely on shortest-path calculations, modern delivery systems use predictive analytics to determine the most efficient routes.
Predictive routing considers variables such as:
- Historical traffic patterns
- Weather conditions
- Courier performance history
- Delivery density in an area
- Time-of-day congestion trends
Batch delivery optimization is another important technique. When multiple orders are heading toward nearby destinations, the system groups them to reduce travel distance and fuel consumption.
Benefits of predictive route optimization include:
- Reduced delivery times
- Lower operational expenses
- Improved courier productivity
- Increased delivery accuracy
- Better customer satisfaction
These capabilities are often integrated during on demand delivery app development to ensure logistics systems can scale efficiently without increasing delivery complexity.
Importance Of Scalable Backend Infrastructure Design For Platforms
Backend infrastructure determines how well delivery platforms handle high transaction volumes. Microservices architecture is commonly used to separate responsibilities such as order processing, courier tracking, payment handling, and notifications.
Scalable backend systems typically include:
- Load-balanced application servers
- Distributed databases
- Event-stream processing systems
- Cloud-based storage solutions
- Fault-tolerant messaging queues
This modular approach prevents system-wide failures when individual components experience high load.
Infrastructure scalability also plays a role in determining delivery app development cost, since systems designed for elasticity require cloud orchestration, monitoring tools, and redundancy planning.
Without scalable backend architecture, delivery platforms risk downtime during peak usage periods such as holidays or promotional events.
Improving Customer Experience With Status Updates And Notifications
Customer experience in delivery platforms depends heavily on transparency and communication. Automated notifications keep customers informed about each stage of the delivery lifecycle.
Typical notification stages include:
- Order confirmation
- Vendor preparation updates
- Courier assignment
- Pickup confirmation
- Delivery arrival alerts
Real-time status tracking reduces uncertainty and builds trust in the platform.
Push notifications, SMS alerts, and in-app tracking interfaces all work together to maintain engagement. Delivery platforms also use predictive arrival estimates to set accurate expectations.
From a system design perspective, notification services must be asynchronous and fault-tolerant to ensure reliable message delivery across different devices and network conditions.
Security And Payment Synchronization In Delivery Apps Platforms
Secure payment processing is essential in delivery ecosystems. Payment gateways must synchronize transaction confirmation with order management systems to prevent fulfillment errors.
Security layers in delivery applications typically include:
- Tokenized payment data storage
- End-to-end encryption
- Fraud detection monitoring
- Multi-factor authentication
- Secure API communication
Payment synchronization ensures that vendors receive confirmed orders only after successful transaction authorization.
Refund workflows must also be automated to handle cancellations or delivery failures without manual intervention.
Security architecture is particularly important in on demand delivery app development because financial transactions occur continuously and at high volume.
Reliable payment synchronization protects both platform operators and users from transactional inconsistencies.
Future Trends In Automated Logistics Coordination Tech Systems
Delivery coordination technology continues to evolve with advances in artificial intelligence, automation, and robotics. Emerging systems aim to reduce manual logistics intervention while improving delivery speed and reliability.
Some important trends shaping delivery coordination include:
- AI-powered demand forecasting
- Autonomous delivery vehicle integration
- Drone-based last-mile delivery trials
- Hyperlocal warehouse automation
- Real-time supply chain analytics
These technologies will allow delivery platforms to operate with greater autonomy and predictive accuracy.
Automation will also improve courier utilization efficiency by reducing idle time and improving dispatch precision. Logistics platforms are expected to become increasingly data-driven, with real-time analytics guiding operational decisions.
As urban delivery demand continues to grow, coordination systems will become more sophisticated and resilient.
Conclusion
Efficient delivery coordination depends on the seamless interaction between dispatch algorithms, tracking systems, backend infrastructure, and customer communication channels. When these components operate together in real time, delivery platforms can manage complex logistics workflows with consistency and reliability. Advances in predictive analytics, automation, and scalable system design continue to improve delivery performance across industries. As logistics technology matures, delivery ecosystems will become faster, smarter, and more resilient in handling growing consumer expectations and operational complexity.